AI-enabled farming opportunities
 Source: Critical Future 2021
Source: Critical Future 2021Client services
Critical Future is uniquely equipped to consult on AI in farming, as we both develop AI systems with PhD experts in machine learning and provide strategic consultancy services.
Critical Future was recently engaged by a world leader in bioscience and farming, with over $10 billion in revenue and 20,000 employees, to analyse the AI precision farming market.
Goals for client:
- Analysis of the market of precision livestock farming (PLF).
- Competitive positioning.
- Partner strategy.
- Identifying business models which would enable win-win partnerships.
- Identifying opportunities and sizing.
What Critical Future did:
We worked closely with our client to prepare a full report on how to:
- capture the market through optimal competitive positioning and partnership strategy
- continue their precision animal farming activities in other areas, with our team’s support.
Our report highlighted:
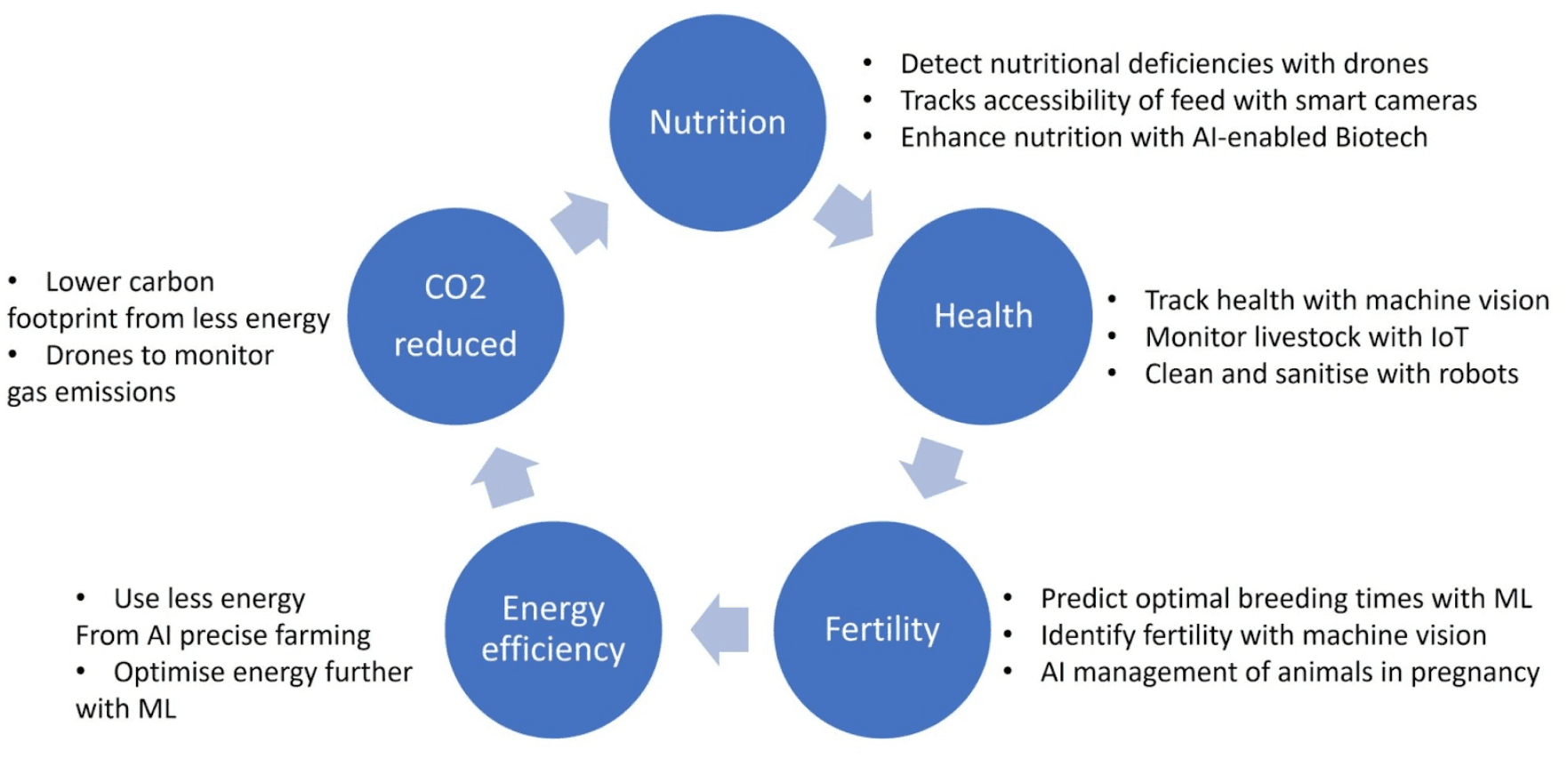
Need for productivity drivers such as AI
Our market analysis revealed that the consumption of animal products (meat, eggs, and milk) will increase by 70% by 2050, while the number of farmers is steadily decreasing.
Thus, our analysis underlined that precision livestock farming (PLF) is the solution for the management of farms, creating an opportunity for our client in the market.
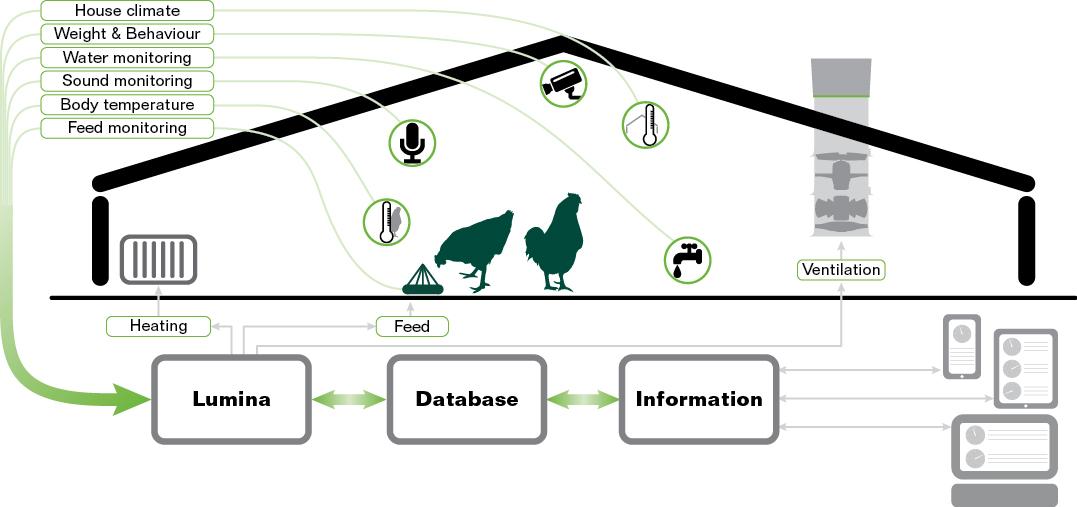
image credits: fancom.com

Need for integration of AI with other advanced tech
Robots, drones, 3D printing, virtual reality, blockchain and Internet of Things are state-of-the-art trends in farming. When used responsibly by farmers, they can achieve more productive, efficient and sustainable farm operations.
Examples of AI and advanced tech used in farming
Machine vision
This technique for monitoring the health of farm animals / dairy cattle with a high degree of accuracy uses a camera and artificial intelligence (AI) to achieve a “smart” cowhouse.
Detailed observation by AI-powered image analysis enables early detection of injuries and illnesses that could impact the quantity and quality of milk production.
Drones
These are used to inspect the herd or fences or to help herd cows from fields to barns. Modern dairy is using drones to map, inspect and photograph pastures in order to detect growth.
Algorithms enable drones to identify cows specifically and avoid confusing them with deer or similar animals.
Temperature detection allows farmers to identify abnormal behaviour in the cow, such as lameness, illness or calving.
Robots
In the livestock sector, robots increase efficiencies and replace expensive or unavailable labour.
Other uses for robots include:
- cleaning and sanitizing the barn, allowing for better biosecurity measures that will lead to healthier conditions for the animals
- medical and health assessments using transponders or sensors.
3D printing
The primary application of 3D printing is for machine parts, which may be of particular interest to rural farmers.
Depending on the part needed, this could save valuable time and money.
Augmented reality
Augmented reality (AR) can be used with reliable sensor data for a vet to deliver appropriate recommendations for disease management. AR can scale up veterinary medicine across farming at a lower cost.
Virtual reality
VR’s applications in farming vary from farm tours to veterinary training, with positive impacts on safety and efficiency. Employees learn to identify potential hazards and experience hazardous situations in a realistic simulated environment, enhancing learning experiences without the risk of harm. VR also reduces labour costs by replacing a number of hands-on health and safety training positions
Blockchain
Consumers are increasingly becoming interested in where their food comes from and how it is produced. Blockchain can connect all aspects of the supply chain, from producer to consumer, and allow for food traceability and safety. From an agriculture and food perspective, offering this type of information to consumers will become a competitive advantage.
Internet of Things
Together, these technologies are creating opportunities within farming for increased efficiencies, profitability and production. The connectivity of these technologies is made possible through the Internet of Things (IoT).
Applications of AI in the farming sector
AI in milk farming
Using sensor data and real-world behaviour, AI technology can detect when a cow is walking, drinking or eating.
This is most useful for large barns, where it is impossible to keep up with every individual cow. With facial recognition, AI can help identify each cow uniquely. This helps farmers provide better treatment to the cows
AI in meat farming
AI systems can monitor vulnerable piglets for squeals of distress, or recognize facial expressions to tell if a sheep is in pain. They can detect different parts of a sheep’s face and compare them with standardized facial patterns provided by veterinarians to diagnose the pain.
AI in poultry farming
AI-enabled robots optimize poultry farming by:
- keeping birds moving for health benefits
- doing repetitive work like feeding and removing manure
- counting, collecting and packing eggs.
AI in fish farming
Underwater robots can easily examine and repair the nets of aquapods.
Drones can provide applications for aquaculture both above and beneath the water. They can easily monitor offshore fish farms and inspect underwater nets for damage and holes. They can also provide fish stock information and track environmental changes.
Sensors can be used in aquaculture to collect data such as oxygen levels, pH, salinity and the pollution level of water. They can detect the hunger level of the fish, which helps farmers or even robots feed them accordingly. Automated recirculation systems can circulate the water according to the information collected by sensors.
AI for sustainable farming
As AI optimizes farming, it removes waste and conserves energy. Specific ML models can predict the optimal times to use energy, optimizing its usage. There is a direct benefit to sustainability as farming reduces its carbon footprint.
-
Matthew Stewart
AI ConsultantMatthew Stewart is a Senior AI Engineer at Critical Future, and a PhD in Machine Learning at Harvard....
view profile -
Prabhakar Ray
Prabhakar Ray is a PhD in Robotics & AI at Kings College London. Prabhakar has a Master in Artificial...
view profile -
Gabriela Gálvez
AI ConsultantMSc in Artificial Intelligence for Business Transformation Master in Business and International...
view profile -
Adam Riccoboni
CEO & Managing DirectorAdam Riccoboni is the founder and CEO of Critical Future. He is an award-winning entrepreneur, founder...
view profile






